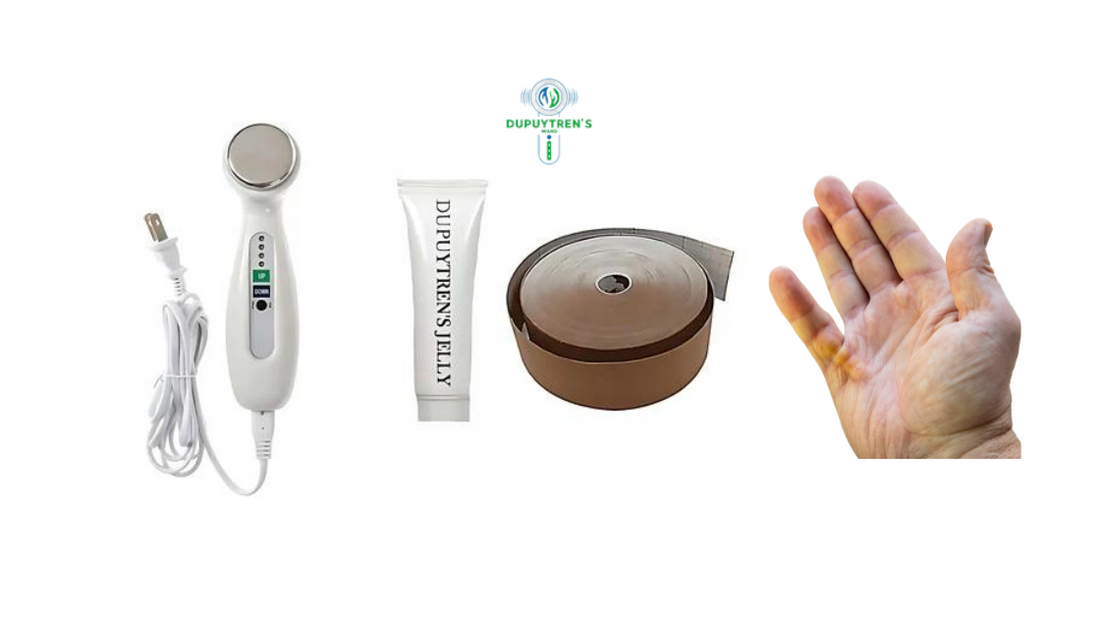
How Dupuytren's Wand Works: A Comprehensive Guide
Share
Dupuytren's Contracture is a condition that causes the fingers to curl inward due to the thickening of the fascia, a layer of tissue under the skin of the palm and fingers. This can make everyday tasks difficult. Finding effective treatment is crucial for those affected. One innovative solution is the Dupuytren's Wand. But how does this device work? In this blog, we’ll explore the science and functionality behind the Dupuytren's Wand to help you understand its benefits and usage.
Understanding Dupuytren's Contracture
Before diving into how the Dupuytren's Wand works, it's important to understand Dupuytren's Contracture. This condition involves the thickening of the fascia, which can form knots and eventually create a cord that pulls one or more fingers into a bent position.
The Need for Non-Surgical Treatment
Traditional treatments for Dupuytren's Contracture include surgery, needle aponeurotomy, and enzyme injections. While these methods can be effective, they come with risks such as infection, nerve damage, and extended recovery periods. This is where the Dupuytren's Wand offers a promising alternative, providing a non-invasive, low-risk treatment option.
Science Behind Dupuytren's Wand
The Dupuytren's Wand is designed to reduce the thickened fascia and improve finger mobility through a combination of heat, massage, and specialized frequencies.
- Heat Therapy
- The Dupuytren's Wand uses controlled heat to penetrate the skin and underlying tissues. This heat increases blood flow to the affected area, which can help to soften and break down the thickened fascia. Enhanced circulation promotes healing and flexibility, reducing the stiffness associated with Dupuytren's Contracture.
- Massage Action
- Integrated into the Dupuytren's Wand is a gentle massage mechanism. This massage helps to further soften the tight cords and fascia, making them more pliable. Regular massage therapy has been shown to improve the elasticity of tissues, which is crucial for restoring normal finger movement.
- Specialized Frequencies
- One of the unique aspects of the Dupuytren's Wand is its use of specialized frequencies. These frequencies are designed to target the fibrous tissue specifically, promoting cellular repair and regeneration. The gentle vibrations encourage the breakdown of the collagen buildup that characterizes Dupuytren's Contracture.
Using the Dupuytren's Wand: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using the Dupuytren's Wand is straightforward, making it accessible for regular use at home. Here’s a simple guide on how to use it:
- Preparation
- Ensure your hand is clean and dry. Sit in a comfortable position where you can easily access the affected hand.
- Application of Heat
- Turn on the Dupuytren's Wand Works and allow it to heat up. Once it reaches the desired temperature, apply it to the affected area. Move the wand in slow, circular motions, ensuring even coverage.
- Massage Therapy
- Activate the massage function on the wand. Continue to move the device over the affected cords and fascia, spending extra time on particularly tight areas.
- Duration
- Each session should last about 10-15 minutes. Consistent use is key, so aim to use the wand daily or as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Aftercare
- After the session, gently stretch your fingers to maintain flexibility. You may also apply a moisturizing lotion to keep the skin hydrated.
Benefits of the Dupuytren's Wand
The Dupuytren's Wand offers several benefits for those suffering from Dupuytren's Contracture:
- Non-Invasive: Unlike surgery, the wand is non-invasive and carries no risk of infection or nerve damage.
- Convenient: It can be used at home, making it a convenient option for regular therapy.
- Cost-Effective: Over time, it may be more cost-effective than repeated medical treatments.
- Improved Mobility: Many users report improved finger mobility and reduced pain after consistent use.
